目標
- 機器學習的目標有很多種,參考李宏毅教授的機器學習課程,可以用下面一張圖來概述。
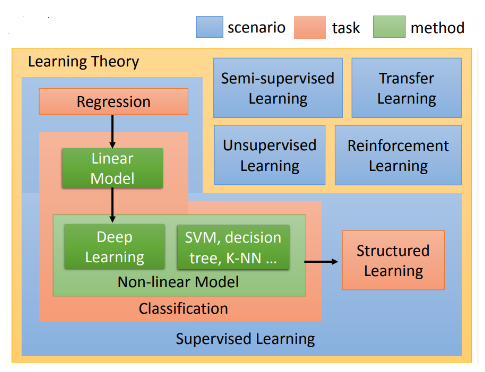
- Task 代表機器學習的目標
- Regression: 透過迴歸來預測值。
- Classification: 處理分類問題。
- Structed Learning: 生成結構化的資訊(現在稱為生成式 AI, GenAI)
- Scenario 代表解決問題的策略
- Supervised Learning: 使用已標記的訓練數據進行訓練
- Semi-supervised Learning: 使用有標記與無標記的訓練數據進行訓練
- Unsupervised Learning: 不使用標記的訓練數據進行訓據,由模型自行發現模式與結構
- Reinforcement Learning: 透過「獎勵」與「懲罰」來學習。
- Transfer Learning: 將一個任務學習到的知識應用到相關的新任務
- Method 指應用的方法
- Linear Model
- Deep Learning
- SVM
- Decision Tree
- KNN
- Task 代表機器學習的目標
線性迴歸
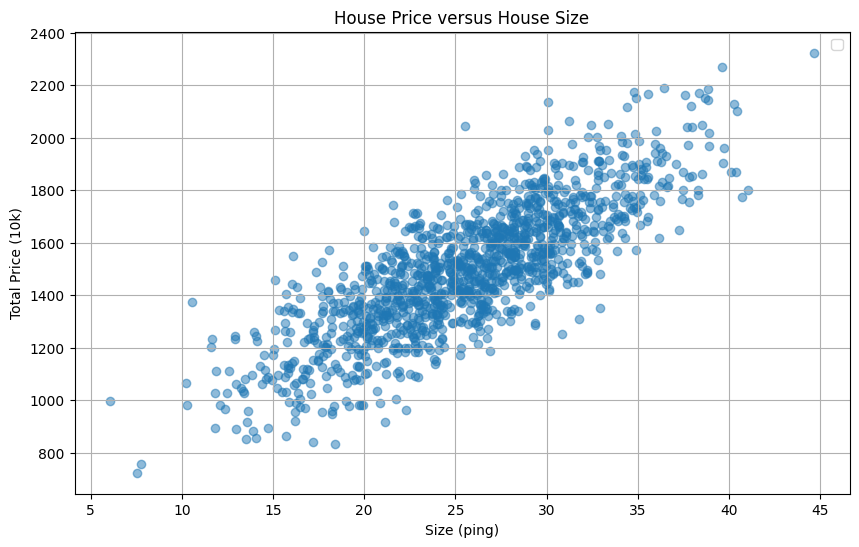
暴力解
- 假設我們大概知道答案的區間,我們可以暴力求解,將每一個 w, b 代入求最小的 (w, b) 組合
- 這個方法的缺點是,計算量很大,且我們求值的方式不是連續的,精準度不夠。
import sys
areas = data[:,0]
prices = data[:,1]
def compute_loss(y_pred, y):
return (y_pred - y)**2
best_w = 0.
best_b = 0.
min_loss = sys.float_info.max
# 猜 w=30-50, step = 0.1
# 猜 b=200-600 step = 1
for i in range(200):
for j in range(400):
w = 30 + i*0.1
b = 200 + j*1
loss = 0.
for area, price in zip(areas, prices):
y_pred = w * area + b
loss += compute_loss(y_pred, price)
if loss < min_loss:
min_loss = loss
best_w = w
best_b = b
w=35.1b=599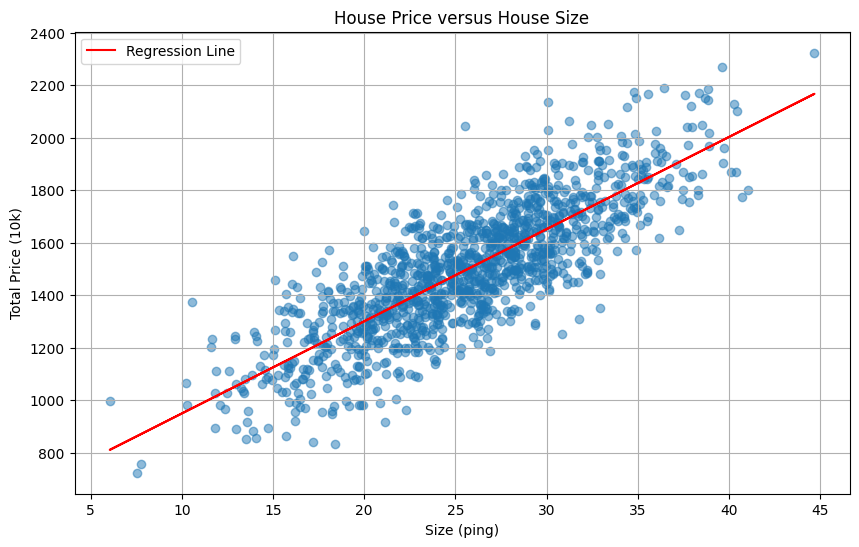
線性代數解法
- 假如我們學過線性代數,我們想得到它的歸性迴歸方程式,我們的作法會是:
設迴歸方程式為 $$\text{y}=\text{wx}+\text{b}\quad\quad (1)$$
我們要求最小平方差 $$\text{L}=\sum_{i=0}^n(\text{y}_i-\text{y})^2\quad\quad (2)$$
將 (1) 代入 (2)
$$\text{L}=\sum_{i=0}^n(\text{y}_i-\text{wx}-\text{b})^2\quad\quad (3)$$學過線性代數,我們知道要求極值,可以對其求導數為0,並設 w 與 b 互不為函數,故我們對其個別做偏微分等於0。 $$\frac{\partial\text{L}}{\partial\text{w}}=0$$
$$\frac{\partial\text{L}}{\partial\text{b}}=0$$
對 b 做偏微分 $$\frac{\partial\text{L}}{\partial\text{b}}=-2\sum_{i=0}^n(\text{y}_i-\text{wx}_i-\text{b})=0$$
$$\sum_{i=0}^n(\text{y}_i-\text{wx}_i-\text{b})=0$$
$$\sum_{i=0}^n\text{y}_i-\text{w}\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i-\text{nb}=0$$
$$\text{n}\bar{\text{y}}-\text{n}\bar{\text{wx}}-\text{nb}=0$$
$$\text{b}=\bar{\text{y}}-\text{w}\bar{\text{x}}\quad\quad (4)$$
對 w 做偏微分 $$\frac{\partial\text{L}}{\partial\text{w}}=-2\sum_{i=0}^n\text{x}_i(\text{y}_i-\text{wx}_i-\text{b})=0$$
$$\sum_{i=0}^n\text{x}_i(\text{y}_i-\text{wx}_i-\text{b})=0$$
$$\sum_{i=0}^n\text{x}_i\text{y}_i-\text{w}\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i^2-\text{b}\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i=0$$
- 代入 (4)
$$\sum_{i=0}^n\text{x}_i\text{y}_i-\text{w}\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i^2-(\bar{\text{y}}-\text{w}\bar{\text{x}})\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i=0$$
$$\sum_{i=0}^n\text{x}_i\text{y}_i-\text{w}\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i^2-\bar{\text{y}}\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i+\text{w}\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i\bar{\text{x}}=0$$
$$\text{w}(\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i\bar{\text{x}}-\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i^2)=\bar{\text{y}}\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i-\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i\text{y}_i$$
$$\text{w}(\text{n}\bar{\text{x}}^2-\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i^2)=\text{n}\bar{\text{x}}\bar{\text{y}}-\sum _{i=0}^n\text{x}_i\text{y}_i$$
$$\text{w}=\frac{\sum\text{x}_i\text{y}_i-\text{n}\bar{\text{x}}\bar{\text{y}}}{\sum\text{x}_i^2-\text{n}\bar{\text{x}}^2}$$
$$\text{w}=\frac{\sum\text{y}_i(\text{x}_i-\bar{\text{x}})}{\sum\text{x}_i(\text{x}_i-\bar{\text{x}})}$$
$$\text{w}=\frac{\sum(\text{y}-\bar{\text{y}})(\text{x}-\bar{\text{x}})}{\sum(\text{x}_i-\bar{\text{x}})^2}$$
$$\text{w}=\frac{S_{XY}}{S_{XX}}\quad\quad(5)$$
換言之,我們可以透過 (4) 與 (5) 式直接求得迴歸方程式 $$\text{y}=\frac{S_{XY}}{S_{XX}}\text{x}+(\bar{\text{y}}-\frac{S_{XY}}{S_{XX}}\bar{\text{x}})$$
其中
$$S_{XY}=\sum(\text{x}_i-\bar{\text{x}})(\text{y}_i-\bar{\text{y}})=\sum\text{x}_i\text{y}_i-\text{n}\bar{\text{x}}\bar{\text{y}}$$
$$S_{XX}=\sum(\text{x}_i-\bar{\text{x}})^2=\sum\text{x}_i^2-\text{n}\bar{\text{x}}^2$$
直接運用於 sample:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt meanx = data[:, 0].mean() meany = data[:, 1].mean() sxy = 0.0 sxx = 0.0 for i in range(data.shape[0]): sxy += (data[i,0] - meanx)*(data[i,1] - meany) sxx += (data[i,0] - meanx)**2 w = sxy/sxx b = meany - w*meanx plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.scatter(data[:, 0], data[:, 1], alpha=0.5) plt.plot(data[:, 0], w*data[:, 0] + b, color='red', label='Regression Line') plt.xlabel('Size (ping)') plt.ylabel('Total Price (10k)') plt.title('House Price versus House Size') plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.show() print(f"w = {w:.4f}") print(f"b = {b:.4f}")
w = 34.9738b = 602.5411
梯度下降(gradient descent)
- 但事實上,在機器學習的領域要處理的不一定是上述這種只有兩維的問題,多維的問題會有多個梯度為0的地方,代表我們需要求出全部梯度為0的地方,再逐一代入我們的 loss function,最後找出 loss 最小的一組答案。
- 再者是,加入 activation function 後的方程式,變得並非上述案例中的容易微分。
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
# 1. 資料正規化函數
def normalize_data(data):
return (data - np.mean(data, axis=0)) / np.std(data, axis=0)
# 2. 建立並訓練模型的函數
def train_linear_regression(x_norm, y_norm, learning_rate=0.01, epochs=10):
# 建立模型
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(1, input_shape=(1,))
])
# 編譯模型
optimizer = keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=learning_rate)
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss='mse')
# 用於記錄訓練過程的參數
history = {'w': [], 'b': [], 'loss': []}
class ParameterHistory(keras.callbacks.Callback):
def on_epoch_begin(self, epoch, logs=None):
w = self.model.layers[0].get_weights()[0][0][0]
b = self.model.layers[0].get_weights()[1][0]
loss = self.model.evaluate(x_norm, y_norm, verbose=0)
history['w'].append(w)
history['b'].append(b)
history['loss'].append(loss)
# 訓練模型
parameter_history = ParameterHistory()
model.fit(x_norm, y_norm, epochs=epochs, verbose=0, callbacks=[parameter_history])
# 記錄最後一次的參數
w = model.layers[0].get_weights()[0][0][0]
b = model.layers[0].get_weights()[1][0]
loss = model.evaluate(x_norm, y_norm, verbose=0)
history['w'].append(w)
history['b'].append(b)
history['loss'].append(loss)
return model, history
# 3. 視覺化函數
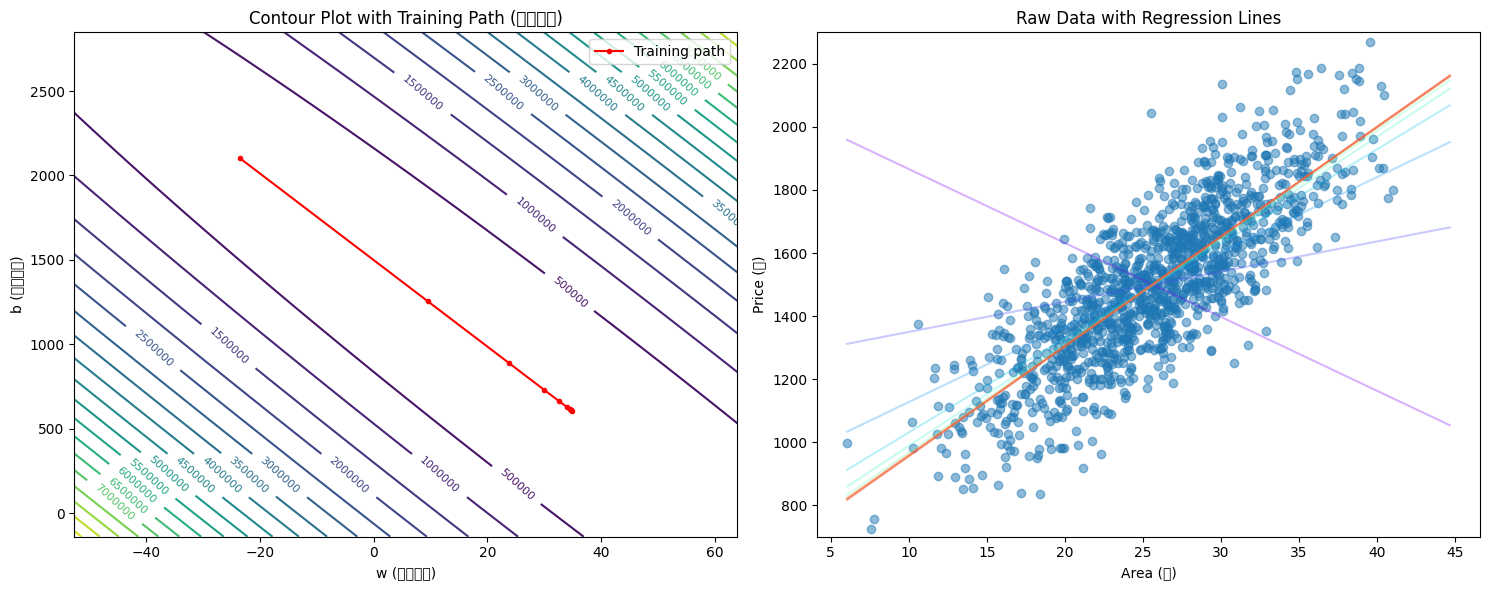
def plot_training_process(x_raw, y_raw, x_norm, y_norm, history):
# 創建圖表
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 6))
# 將正規化的係數轉換回原始尺度
w_raw_history = [w * np.std(y_raw) / np.std(x_raw) for w in history['w']]
b_raw_history = [(b * np.std(y_raw) + np.mean(y_raw) -
w * np.std(y_raw) * np.mean(x_raw) / np.std(x_raw))
for w, b in zip(history['w'], history['b'])]
# Contour plot with raw scale
margin_w = (max(w_raw_history) - min(w_raw_history)) * 0.5
margin_b = (max(b_raw_history) - min(b_raw_history)) * 0.5
w_raw_range = np.linspace(min(w_raw_history)-margin_w, max(w_raw_history)+margin_w, 100)
b_raw_range = np.linspace(min(b_raw_history)-margin_b, max(b_raw_history)+margin_b, 100)
W_RAW, B_RAW = np.meshgrid(w_raw_range, b_raw_range)
Z = np.zeros_like(W_RAW)
# 計算每個點的 MSE(在原始尺度上)
for i in range(W_RAW.shape[0]):
for j in range(W_RAW.shape[1]):
y_pred = W_RAW[i,j] * x_raw + B_RAW[i,j]
Z[i,j] = np.mean((y_pred - y_raw) ** 2)
CS = ax1.contour(W_RAW, B_RAW, Z, levels=20)
ax1.clabel(CS, inline=True, fontsize=8)
ax1.plot(w_raw_history, b_raw_history, 'r.-', label='Training path')
ax1.set_xlabel('w (原始尺度)')
ax1.set_ylabel('b (原始尺度)')
ax1.set_title('Contour Plot with Training Path (原始尺度)')
ax1.legend()
# Raw data scatter plot with regression lines
ax2.scatter(x_raw, y_raw, alpha=0.5, label='Raw data')
ax2.set_ylim(700, 2300)
# 繪製每一輪的回歸線
x_plot = np.linspace(min(x_raw), max(x_raw), 100)
colors = cm.rainbow(np.linspace(0, 1, len(w_raw_history)))
for i, (w, b) in enumerate(zip(w_raw_history, b_raw_history)):
y_plot = w * x_plot + b
ax2.plot(x_plot, y_plot, color=colors[i], alpha=0.3)
ax2.set_xlabel('Area (坪)')
ax2.set_ylabel('Price (萬)')
ax2.set_title('Raw Data with Regression Lines')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 載入數據
data = load_data()
x_raw, y_raw = data[:, 0], data[:, 1]
# 轉換為 TensorFlow 格式
x_raw = x_raw.reshape(-1, 1)
y_raw = y_raw.reshape(-1, 1)
# 正規化數據
x_norm = normalize_data(x_raw)
y_norm = normalize_data(y_raw)
# 訓練模型
model, history = train_linear_regression(x_norm, y_norm)
# 視覺化結果
plot_training_process(x_raw.flatten(), y_raw.flatten(),
x_norm.flatten(), y_norm.flatten(), history)
# 輸出最終結果
final_w = history['w'][-1]
final_b = history['b'][-1]
final_loss = history['loss'][-1]
# 將係數轉換回原始尺度
w_raw = final_w * np.std(y_raw) / np.std(x_raw)
b_raw = (final_b * np.std(y_raw) + np.mean(y_raw) -
final_w * np.std(y_raw) * np.mean(x_raw) / np.std(x_raw))
print(f"Final equation: y = {w_raw[0]:.2f}x + {b_raw[0]:.2f}")
print(f"Final normalized loss: {final_loss:.6f}")
批次訓練(Batch)的概念
- 我們可以在不同的時機點來更新 w 與 b,假設我們的訓練次數為 3000,那 epochs 為3000。且樣本數為 1000。
- 批次訓練(batch training),代表的是我們總共做 3000 次的更新,每次都是利用全部 1000 筆樣本算出來的 dw 與 db 去做調整。
- SGD(Stochastic gradient descent),代表我們做 3000 * 1000 次的更新,每一個樣本計算出 dw 與 db 就立即去調整。
- 小批次訓練(mini-batch training)則是介於批次訓練與 SGD 之間,假設我們每 200 個樣本做一次更新,實際上會做 3000 * 5 次更新。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class LinearRegression:
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.0000001):
self.w = 0.0
self.b = 0.0
self.lr = learning_rate
self.loss_history = []
def predict(self, X):
return self.w * X + self.b
def compute_loss(self, X, y):
y_pred = self.predict(X)
return np.mean((y_pred - y) ** 2)
def compute_gradients(self, X, y):
y_pred = self.predict(X)
error = y_pred - y
dw = np.mean(2 * error * X)
db = np.mean(2 * error)
return dw, db
def train_batch(self, X, y, epochs=3000):
"""Full batch gradient descent"""
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Compute gradients using all data
dw, db = self.compute_gradients(X, y)
# Update parameters
self.w -= self.lr * dw
self.b -= self.lr * db
# Record loss
if epoch % 100 == 0:
loss = self.compute_loss(X, y)
self.loss_history.append(loss)
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Loss: {loss:.2f}")
def train_mini_batch(self, X, y, batch_size=2, epochs=3000):
"""Mini-batch gradient descent"""
n_samples = len(X)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Shuffle the data
indices = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X_shuffled = X[indices]
y_shuffled = y[indices]
# Mini-batch training
for i in range(0, n_samples, batch_size):
X_batch = X_shuffled[i:i+batch_size]
y_batch = y_shuffled[i:i+batch_size]
# Compute gradients using batch data
dw, db = self.compute_gradients(X_batch, y_batch)
# Update parameters
self.w -= self.lr * dw
self.b -= self.lr * db
# Record loss for the whole dataset
if epoch % 100 == 0:
loss = self.compute_loss(X, y)
self.loss_history.append(loss)
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Loss: {loss:.2f}")
def train_sgd(self, X, y, epochs=3000):
"""Stochastic gradient descent"""
n_samples = len(X)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Shuffle the data
indices = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X_shuffled = X[indices]
y_shuffled = y[indices]
# SGD training (batch_size = 1)
for i in range(n_samples):
X_sample = X_shuffled[i:i+1]
y_sample = y_shuffled[i:i+1]
# Compute gradients using single sample
dw, db = self.compute_gradients(X_sample, y_sample)
# Update parameters
self.w -= self.lr * dw
self.b -= self.lr * db
# Record loss for the whole dataset
if epoch % 100 == 0:
loss = self.compute_loss(X, y)
self.loss_history.append(loss)
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Loss: {loss:.2f}")
(areas, prices) = load_data()
models = {
'Batch': LinearRegression(learning_rate=1e-7),
'Mini-batch': LinearRegression(learning_rate=1e-7),
'SGD': LinearRegression(learning_rate=5e-8)
}
models['Batch'].train_batch(areas, prices)
models['Mini-batch'].train_mini_batch(areas, prices)
models['SGD'].train_sgd(areas, prices)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for name, model in models.items():
plt.plot(range(0, 3000, 100), model.loss_history, label=name)
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Loss Comparison')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
for name, model in models.items():
print(f"\n{name} Results:")
print(f"w = {model.w:.6f}")
print(f"b = {model.b:.6f}")
print(f"Final Loss = {model.loss_histroy[-1]:.2f}")
從更新次數來看,SGD 的更新次數 > 小批次訓練 > 批次訓練,SGD 所耗的時間同樣也比小批次訓練與批次訓練長,但實際上 loss 收斂的情形也比較好嗎?
從下圖比較可見,收斂情況最佳的反而是小批次訓練,我們比較三種方法,總結一下成果:
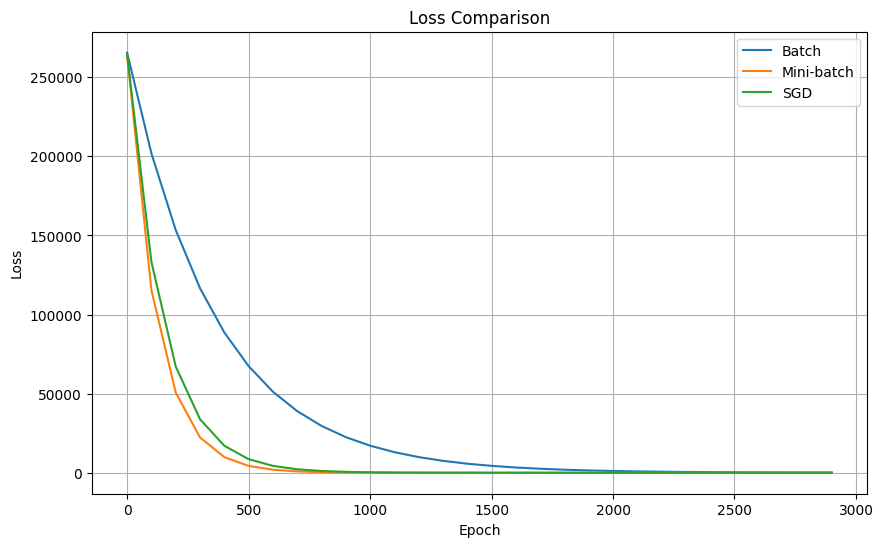
批次訓練 Batch Gradient Descent (BGD)
- 每次更新使用所有數據
- 穩定但計算量大
- 容易找到局部最優解
小批次訓練 Mini-batch Gradient Descent
- 每次使用一小批數據
- 平衡了計算效率和更新穩定性
- 常用於實際應用
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
- 每次只使用一個樣本
- 更新頻繁,收斂較快但不穩定
- 需要較小的學習率
損失函數(loss function)
損失函數是用來衡量模型預測值與實際值之間差異的函數,以下是幾個常見的損失函數:
均方誤差(Mean Squared Error, MSE)
- 常用於迴歸問題
- 對異常值敏感 $$ \text{MSE}=\frac{1}{\text{n}}\sum^n(\text{y}_\text{pred}-\text{y} _\text{true})^2 $$
交叉熵損失(Cross Entropy Loss)
- 常用於分類問題
- 衡量兩個概率分布之間的差異
- 又分為二元交叉熵和多類別交叉熵
- 二元交叉熵(Binary Cross Entropy) $$ \text{BCE}=-(\text{y}_\text{true}\times \log(\text{y} _\text{pred})+(1-\text{y} _\text{true})\times \log(1-\text{y} _\text{pred})) $$
- 多類別交叉熵(Categorical Cross Entropy) $$ \text{CCE}=-\sum^n((\text{y} _\text{true})_i\times\log((\text{y} _\text{true})_i)) $$
平均絕對誤差(Mean Absolute Error, MAE)
- 用於迴歸問題
- 相較 MSE 對異常值不那麼敏感 $$ \text{MAE}=\frac{1}{\text{n}}\sum^n|\text{y} _\text{pred}-\text{y} _\text{true}| $$
Hinge Loss
- 主要用於支持向量機(SVM)
- 特別適合最大間隔分類問題 $$ \text{HL} = \max(0, 1-\text{y} _\text{pred}\times\text{y} _\text{true}) $$
在選擇損失函數時需考慮
- 問題類型(分類還是迴歸)
- 數據分布特性
- 對異常值的敏感度要求
- 模型的收斂速度要求
L1/L2 正則化(L1/L2 Regularization)
在考慮有多個特徵、且帶有 outlier 或雜訊時
L1 正則化 (Lasso Regression)
- Lasso (Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator)
- 定義:在損失函數中加入參數的絕對值項 $$ \text{Loss} = \text{MSE} + \lambda \times \sum|w| $$
- 特點:
- 傾向於產生稀疏解(某些參數會變成0)
- 適合用於特徵選擇
- 對異常值較不敏感
L2 正則化 (Ridge Regression)
- 定義:在損失函數中加入參數的平方項 $$ \text{Loss} = \text{MSE} + \lambda \times \sum(w^2) $$
- 特點:
- 傾向於使所有參數值變小但不為0
- 計算導數較簡單
- 對共線性(多重共線性)問題有好處
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 生成合成數據
np.random.seed(42)
def generate_synthetic_data(n_samples=100):
# 生成基本特徵
X1 = np.random.normal(0, 1, n_samples) # 面積
X2 = np.random.normal(0, 1, n_samples) # 房齡
# 生成共線性特徵(與面積高度相關的特徵,如房間數)
X3 = 0.8 * X1 + 0.2 * np.random.normal(0, 1, n_samples)
# 生成噪音特徵(完全無關的特徵)
X4 = np.random.normal(0, 1, n_samples)
# 組合特徵
X = np.column_stack([X1, X2, X3, X4])
# 生成目標值(房價)
# 主要由X1和X2決定,X3有少許影響,X4完全不影響
y = 3 * X1 + 2 * X2 + 0.5 * X3 + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, n_samples)
return X, y
class RegularizedRegression:
def __init__(self, learning_rate=1e-7, reg_type='l2', lambda_reg=0.1):
self.w = 0.
self.b = 0.
self.lr = learning_rate
self.reg_type = reg_type
self.lambda_reg = lambda_reg
self.loss_history = []
def predict(self, X):
return self.w * X + self.b
def compute_loss(self, X, y):
y_pred = self.predict(X)
mse = np.mean((y_pred - y) ** 2)
if self.reg_type == 'l1':
reg_term = self.lambda_reg * np.abs(self.w)
elif self.reg_type == 'l2':
reg_term = self.lambda_reg * (self.w ** 2)
else:
reg_term = 0
return mse + reg_term
def compute_gradients(self, X, y):
y_pred = self.predict(X)
error = y_pred - y
# mse 的梯度
dw_mse = np.mean(2 * error * X)
db = np.mean(2 * error)
# 正則化項的梯度
if self.reg_type == 'l1':
dw_reg = self.lambda_reg * np.sign(self.w)
elif self.reg_type == 'l2':
dw_reg = self.lambda_reg * 2 * self.w
else:
dw_reg = 0
dw = dw_mse + dw_reg
return dw, db
def train(self, X, y, epochs=3000):
for epoch in range(epochs):
dw, db = self.compute_gradients(X, y)
self.w -= self.lr * dw
self.b -= self.lr * db
def train(self, X, y, batch_size=None, epochs=3000):
n_samples = len(X)
if batch_size is None:
batch_size = n_samples
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Shuffle the data
indices = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X_shuffled = X[indices]
y_shuffled = y[indices]
# Mini-batch training
for i in range(0, n_samples, batch_size):
X_batch = X_shuffled[i:i+batch_size]
y_batch = y_shuffled[i:i+batch_size]
# Compute gradients using batch data
dw, db = self.compute_gradients(X_batch, y_batch)
# Update parameters
self.w -= self.lr * dw
self.b -= self.lr * db
# Record loss for the whole dataset
if epoch % 100 == 0:
loss = self.compute_loss(X, y)
self.loss_history.append(loss)
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Loss: {loss:.2f}")
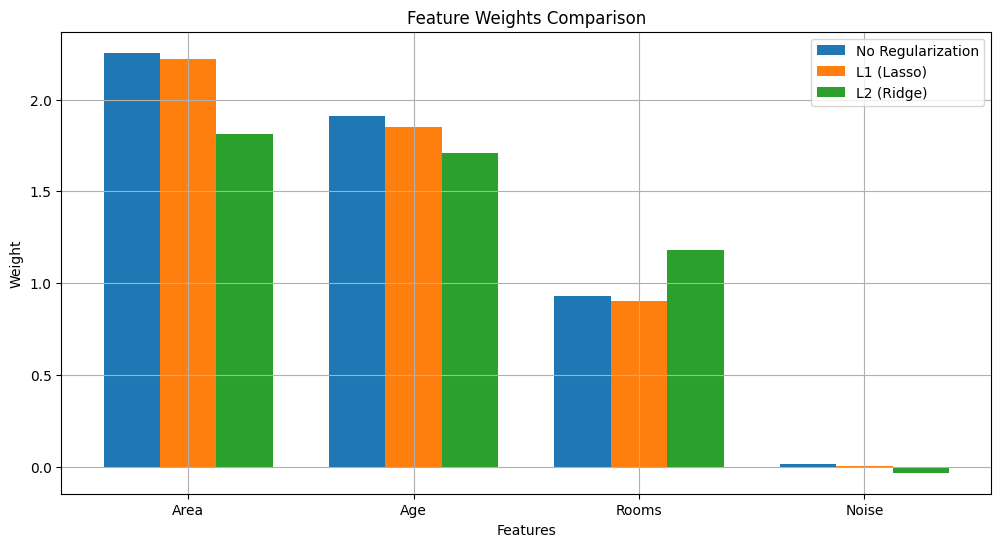
觀察重點:
- L1 正則化(Lasso):
- 傾向於將不重要的特徵(如 Noise)權重設為 0
- 在有共線性的特徵中選擇一個(Area vs Rooms)
- L2 正則化(Ridge):
- 所有權重都被縮小
- 共線性特徵的權重會被平均分配
- 無正則化:
- 可能過度擬合噪音
- 在共線性特徵上表現不穩定
- L1 正則化(Lasso):
從結果可以看出:
- L1 正則化確實將無關特徵(Noise)的權重降到接近 0
- L2 正則化讓所有權重都變得更小,但保持了相對重要性
- 無正則化的模型權重更大,更容易受噪音影響
主要的差異和實作細節:
- 正則化項的加入
- L1:在損失函數中加入
λ * |w| - L2:在損失函數中加入
λ * w²
- 梯度計算
- L1 的梯度:
sign(w) * λ - L2 的梯度:
2 * λ * w
- 超參數 λ (lambda_reg)
- 控制正則化的強度
- 較大的 λ 會產生較小的權重
- 需要通過交叉驗證來選擇適當的值
- 使用場景
- L1:特徵選擇,當你認為只有部分特徵是重要的
- L2:處理共線性,當特徵之間有相關性
激活函數(activation function)
在設計 model 時,不是所有的問題都可以用線性模型來描述,此時我們就需要
- 多層結構(至少一個隱藏層)
- 非線性激活函數
以下為三個重要的激活函數
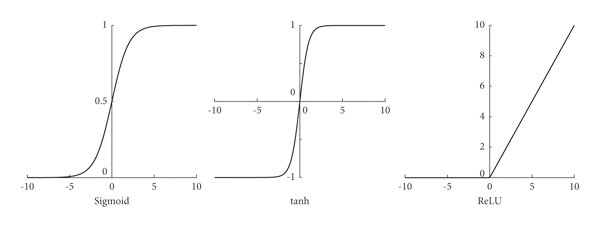
Sigmoid (σ(x) = 1/(1+e^(-x)))
- 輸出範圍:(0,1)
- 優點:適合二分類問題
- 缺點:容易出現梯度消失
ReLU (max(0,x))
- 輸出範圍:[0,∞)
- 優點:計算簡單,不會有梯度消失
- 缺點:Dead ReLU 問題
Tanh (tanh(x))
- 輸出範圍:(-1,1)
- 優點:零中心化
- 缺點:也有梯度消失問題
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Activation:
@staticmethod
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
@staticmethod
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
sx = Activation.sigmoid(x)
return sx * (1 - sx)
@staticmethod
def relu(x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
@staticmethod
def relu_derivative(x):
return np.where(x > 0, 1, 0)
@staticmethod
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
@staticmethod
def tanh_derivative(x):
return 1 - np.tanh(x) ** 2
- 以
xor為例來做以下的機器學習
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Activation:
@staticmethod
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
@staticmethod
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
sx = Activation.sigmoid(x)
return sx * (1 - sx)
@staticmethod
def relu(x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
@staticmethod
def relu_derivative(x):
return np.where(x > 0, 1, 0)
@staticmethod
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
@staticmethod
def tanh_derivative(x):
return 1 - np.tanh(x)**2
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, activation='sigmoid'):
# 網絡架構: 2 -> 4 -> 1
self.W1 = np.random.randn(2, 4) * 0.1 # 輸入層到隱藏層的權重
self.b1 = np.zeros((1, 4)) # 隱藏層偏差
self.W2 = np.random.randn(4, 1) * 0.1 # 隱藏層到輸出層的權重
self.b2 = np.zeros((1, 1)) # 輸出層偏差
# 選擇激活函數
if activation == 'sigmoid':
self.activation = Activation.sigmoid
self.activation_derivative = Activation.sigmoid_derivative
elif activation == 'relu':
self.activation = Activation.relu
self.activation_derivative = Activation.relu_derivative
elif activation == 'tanh':
self.activation = Activation.tanh
self.activation_derivative = Activation.tanh_derivative
self.loss_history = []
def forward(self, X):
# 前向傳播
self.z1 = np.dot(X, self.W1) + self.b1
self.a1 = self.activation(self.z1)
self.z2 = np.dot(self.a1, self.W2) + self.b2
self.a2 = self.activation(self.z2)
return self.a2
def backward(self, X, y, learning_rate=0.1):
m = X.shape[0]
# 計算梯度
dz2 = self.a2 - y
dW2 = np.dot(self.a1.T, dz2) / m
db2 = np.sum(dz2, axis=0, keepdims=True) / m
dz1 = np.dot(dz2, self.W2.T) * self.activation_derivative(self.z1)
dW1 = np.dot(X.T, dz1) / m
db1 = np.sum(dz1, axis=0, keepdims=True) / m
# 更新權重
self.W2 -= learning_rate * dW2
self.b2 -= learning_rate * db2
self.W1 -= learning_rate * dW1
self.b1 -= learning_rate * db1
def train(self, X, y, epochs=10000, learning_rate=0.1):
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 前向傳播
output = self.forward(X)
# 計算損失
loss = np.mean((output - y) ** 2)
self.loss_history.append(loss)
# 反向傳播
self.backward(X, y, learning_rate)
if epoch % 1000 == 0:
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Loss: {loss:.4f}")
def predict(self, X):
return np.round(self.forward(X))
# 準備 XOR 數據
X = np.array([[0,0], [0,1], [1,0], [1,1]])
y = np.array([[0], [1], [1], [0]])
# 訓練不同激活函數的模型
activation_functions = ['sigmoid', 'relu', 'tanh']
models = {}
for activation in activation_functions:
print(f"\nTraining with {activation} activation:")
model = NeuralNetwork(activation=activation)
model.train(X, y)
models[activation] = model
# 繪製損失曲線比較
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for activation, model in models.items():
plt.plot(model.loss_history, label=activation)
plt.xlabel('Iteration')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
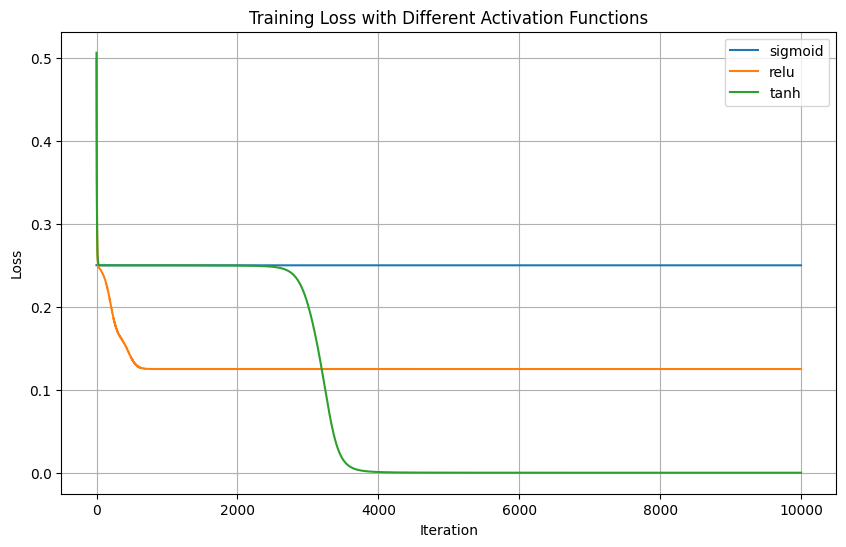
plt.title('Training Loss with Different Activation Functions')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
# 測試預測結果
print("\nPrediction Results:")
for activation, model in models.items():
print(f"\n{activation} activation:")
predictions = model.predict(X)
for x, y_true, y_pred in zip(X, y, predictions):
print(f"Input: {x}, True: {y_true[0]}, Predicted: {y_pred[0]}")
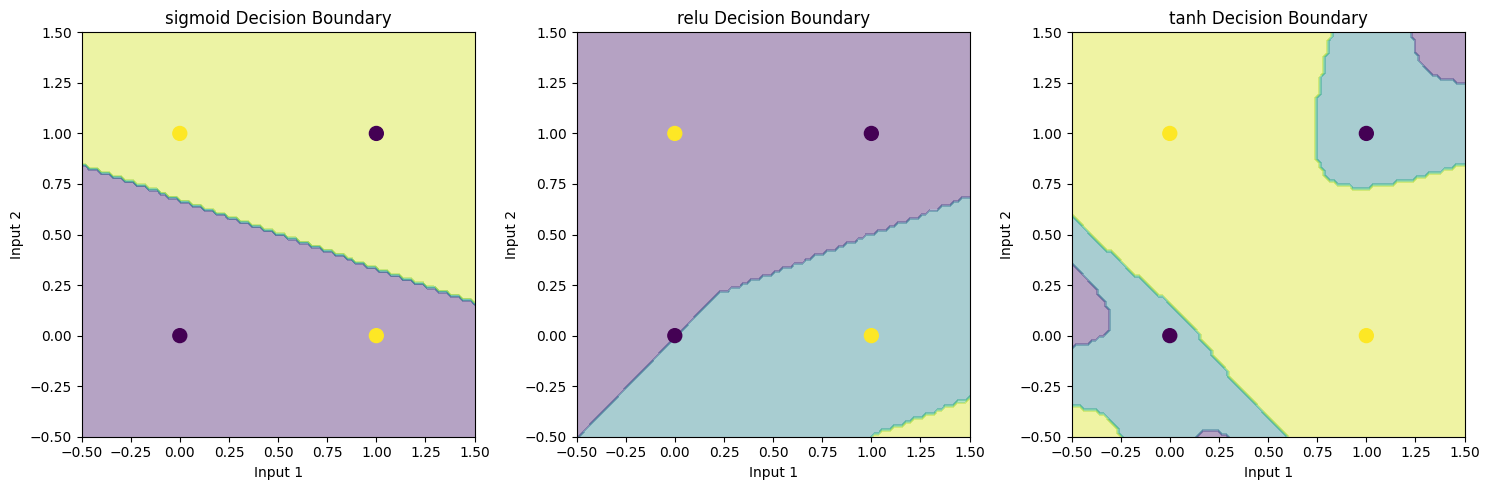
# 視覺化決策邊界
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
for i, (activation, model) in enumerate(models.items()):
plt.subplot(1, 3, i+1)
# 創建網格點
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-0.5, 1.5, 100),
np.linspace(-0.5, 1.5, 100))
grid = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
# 預測
Z = model.predict(grid)
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
# 繪製決策邊界
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, s=100)
plt.title(f'{activation} Decision Boundary')
plt.xlabel('Input 1')
plt.ylabel('Input 2')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Sigmoid
適用時機:
- 二元分類問題的輸出層(因為輸出範圍是 0~1,適合表示機率)
- 需要將輸出限制在 0~1 之間的情境
- 較淺的網路(1-2層)
不建議用在:
- 深層網路的中間層(因為容易發生梯度消失)
- 需要快速訓練的模型(因為計算exponential較慢)
- 對稱數據的問題(因為不是零中心化)
ReLU
適用時機:
- 深層網路的隱藏層(現代深度學習最常用)
- CNN(卷積神經網路)
- 需要快速訓練的大型網路
- 稀疏激活是可接受的場景
主要優點:
- 計算簡單快速
- 能緩解梯度消失問題
- 能產生稀疏的表示(部分神經元輸出為0)
Tanh
適用時機:
- 需要零中心化輸出的場景(輸出範圍-1~1)
- RNN(循環神經網路)的隱藏層
- 數據本身是歸一化/標準化的情況
- 需要較強的梯度在接近零的區域
實際應用建議:
- 常見的最佳實踐組合:
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self):
self.hidden_activation = ReLU # 隱藏層使用ReLU
self.output_activation = Sigmoid # 二分類輸出層使用Sigmoid
- 根據任務選擇:
- 分類問題:輸出層用Sigmoid(二分類)或Softmax(多分類)
- 回歸問題:輸出層可以不用激活函數
- 特徵提取:中間層優先使用ReLU
- 特殊情況:
- 處理序列數據(如RNN):優先考慮Tanh
- 處理圖像數據(如CNN):優先考慮ReLU
- 如果ReLU表現不佳:可以嘗試LeakyReLU或ELU
其它變體
- Leaky ReLu
- 適用時機:
- 當標準ReLU出現大量"死亡"神經元時
- 需要保留負值信息的場景
- 訓練初期希望網絡快速收斂
f(x) = x if x > 0 else αx # (α通常為0.01)
- ELU (Exponential Linear Unit)
- 適用時機:
- 深層網絡需要更強的正則化
- 對噪聲較敏感的任務
- 需要更快收斂速度的場景
f(x) = x if x > 0 else α(exp(x) - 1)
- SELU (Scaled ELU)
- 適用時機:
- 深層全連接網絡
- 需要自歸一化特性的場景
- 希望避免額外的批標準化層
f(x) = λ(x if x > 0 else α(exp(x) - 1))
- GELU(Gaussian Error Linear Unit)
- 適用時機:
- Transformer架構
- BERT等預訓練模型
- 需要考慮輸入不確定性的場景
f(x) = x * P(X ≤ x)
- Swish
- 適用時機:
- 深層模型
- 需要更好泛化性能的場景
- 計算資源充足的情況
f(x) = x * sigmoid(βx)
Summary
先嘗試 ReLU:
- 最簡單且通常效果不錯
- 計算效率高
- 容易優化
如果遇到問題,按順序嘗試:
- Dead ReLU問題 → Leaky ReLU
- 需要自歸一化 → SELU
- 用於Transformer → GELU
- 追求極致性能 → Swish
特殊情況:
- 需要處理時序數據 → ELU或SELU
- 計算資源受限 → 堅持使用ReLU
- 特別關注梯度流動 → Leaky ReLU或ELU
優化器(Optimizers)
優化器是 backpropagation 時使用的更新策略,常見的優化器有:
隨機梯度下降 SGD(Stochastic Gradient Descent)
- 最佳基本的優化器
- 適用時機:
- 數據量大且資源有限
- 問題較簡單
- 需要較好的泛化性能
class Optimizer: def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01): self.lr = learning_rate def update(self, params, grads): raise NotImplementedError class SGD(Optimizer): def update(self, params, grads): for param, grad in zip(params, grads): param -= self.lr * grad return params動量 Momemtum
- 加入動量項(動態調整學習率),幫助越過局部最小值
- 適用時機:
- 梯度下降震盪嚴重時
- 需要加速收斂
- 有較多局部最小值時
class Momemtum(Optimizer): def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, momemtum=0.9): super().__init__(learning_rate) self.momemtum = momemtum self.velocities = None def update(self, params, grades): if self.velocities is None: self.velocities = [np.zeros_like(param) for param in params] for i (param, grad) in enumerate(zip(params, grads)): self.velocities[i] = self.momentum * self.velocities[i] - self.lr * grad param += self.velocities[i] return params自適應學習率 RMSProp
- 動態調整學習率
- 使用時機:
- 處理非平穩問題
- RNN訓練
- 梯度稀疏的問題
class RMSProp(Optimizer): def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, decay_rate=0.09, epsilon=1e-8): super().__init__(learning_rate) self.decay_rate = decay_rate self.epsilon = epsilon self.cache = None def update(self, params, grads): if self.cache is None: self.cache = [np.zeros_like(param) for param in params] for i, (param, grad) in enumerate(zip(params, grads)): self.cache[i] = self.decay_rate * self.cache[i] + (1 - self.decay_rate) * grad ** 2 param -= self.lr * grad / (np.sqrt(self.cache[i]) + self.epsilon) return paramsAdam
- 結合Momentum和RMSprop的優點
- 使用時機:
- 深度學習的默認選擇
- 需要快速收斂
- 大多數問題
class Adam(Optimizer): def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999, epsilon=1e-8): super().__init__(learning_rate) self.beta1 = beta1 self.beta2 = beta2 self.epsilon = epsilon self.m = None self.v = None self.t = 0 def update(self, params, grads): if self.m is None: self.m = [np.zeros_like(param) for param in params] self.v = [np.zeros_like(param) for param in params] self.t += 1 for i, (param, grad) in enumerate(zip(params, grads)): self.m[i] = self.beta1 * self.m[i] + (1 - self.beta1) * grad self.v[i] = self.beta2 * self.v[i] + (1 - self.beta2) * grad**2 m_hat = self.m[i] / (1 - self.beta1**self.t) v_hat = self.v[i] / (1 - self.beta2**self.t) param -= self.lr * m_hat / (np.sqrt(v_hat) + self.epsilon) return params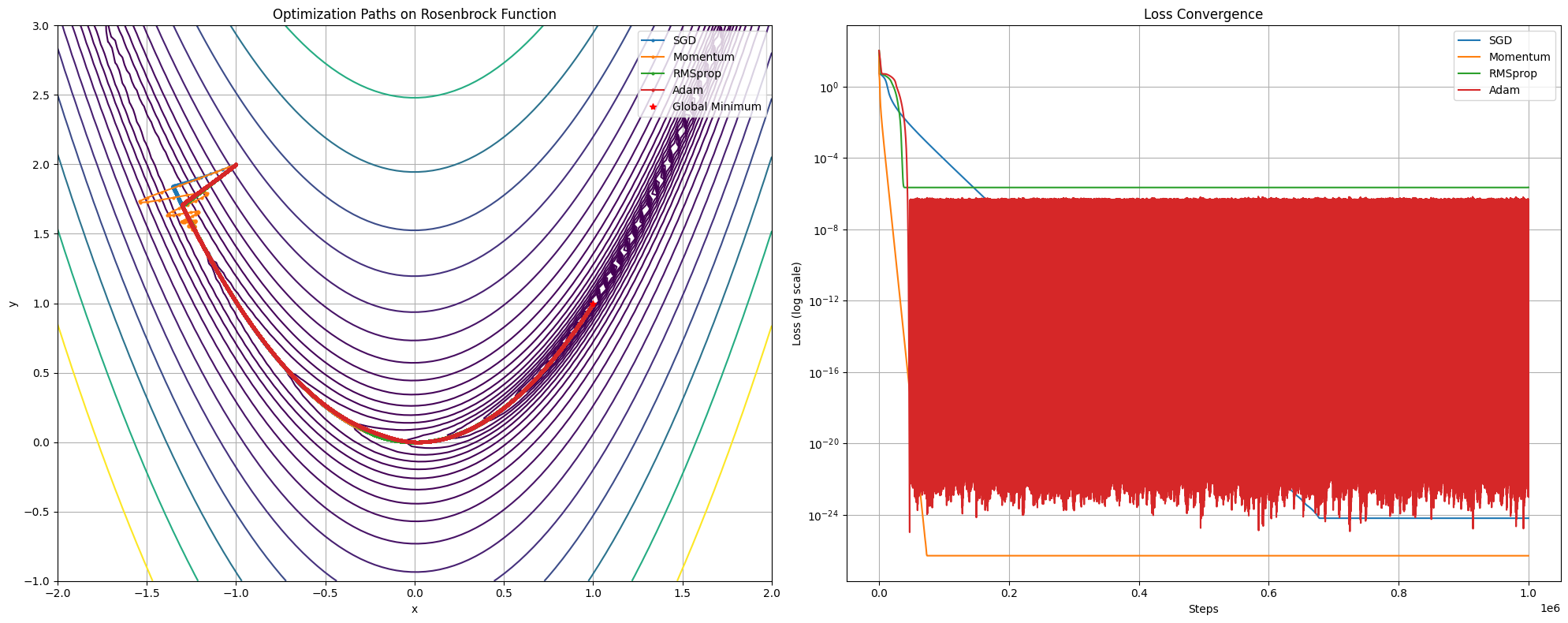
Summary
- 首選Adam:
optimizer = Adam(learning_rate=0.001, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999)- 如果模型較大:
optimizer = AdamW(learning_rate=0.001, weight_decay=0.01)- 如果需要更好的泛化性能:
optimizer = SGD(learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0.9)