1. 認識 IMDB 資料集
- 透過 tensorflow 引入資料集
- 參數
path: 資料的快取位置(相對於 ~/.keras/dataset)。num_words: 整數或 None。單詞按其出現頻率(在訓練集中)進行排序,並且僅保留 num_words 個最常出现的单词。任何較不常出现的单词在序列資料中都將顯示為 oov_char 值。如果為 None,則保留所有單詞。預設值為 None。skip_top: 跳過出現頻率最高的前 N 個單詞(這些單詞可能沒有參考價值)。這些單詞在資料+ 集中將顯示為 oov_char 值。當為 0 時,則不跳過任何單詞。預設值為 0。maxlen: 整數或 None。最大序列長度。任何較長的序列都將被截斷。None 表示不進行截斷。預設值為 None。seed: 整數。用於可重現資料洗牌的種子。start_char: 整數。序列的開頭將標記為此字元。0 通常是填充字元。預設值為 1。oov_char: 整數。詞彙表外字元。由於 num_words 或 skip_top 限制而被刪除的詞彙將替換為此字元。index_from: 整數。使用此索引和更高索引為實際詞彙編制索引。
- 回傳值
- Numpy 陣列的 tuple:
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)。
- Numpy 陣列的 tuple:
- 其中資料集包含了 88585 個相異單字,有很大的單字甚至只有出現一次,這數字對訓練而言非常龐大,且對分類任務沒什麼幫助,所以我們只保留 10000 個最常出現的單字
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import imdb (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = imdb.load_data(num_words=10000) - 參數
- IMDb (Internet Movie Database) 是一個與影視相關的網路資料庫,IMDB 資料集就是從 IMDb 網站收集而來的資料。資料包含了 50000 筆評論,其中包含了 50% 的正面評論與 50% 的負面評論。
print(train_data.shape) print(train_labels.shape) print(test_data.shape) print(test_labels.shape) > (25000,) > (25000,) > (25000,) > (25000,) - 資料的組成是由一連串的數字所組成,如:
\( \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \text{(保留)} & \text{the} & \text{and} & \text{a} & \text{…} & \text{in} & \text{…} & \text{wonderful} & \text{…} & \text{morning} & \text{…} \\ \hline 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & … & 8 & … & 386 & … & 1969 & …\\ \hline \end{array} \)- 每個數字代表一個單字,編號愈前面代表愈常用。
print(train_data[0]) > [1, 14, 22, 16, 43, 530, 973, 1622, ..., 32]- 我們可以用
imdb.get_word_index(path="imdb_word_index.json")來得到這個字典,並試著還原原始評論。 - 注意按引
0~2為留保字,故索引值需位移 3。
dict = imdb.get_word_index(path="imdb_word_index.json") index_to_word = {value: key for key, value in dict.items()} sentence_0 = ' '.join([index_to_word.get(idx, '?') for idx in train_data[0]]) print(sentence_0) > ? this film was just brilliant casting location scenery story direction- labels 是由 1, 0 組成的陣列,代表正評(1)或負評(0)
print(train_labels[:10]) > array([1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0])
2. 準備資料
- 由於目前的測試資料的長度都不一樣長,我們需要預先做整型,方法有二:
- 填補資料中每個串列,使長度相同。
- 做 mutli-hot(k-hot) 轉換。
\( \begin{array}{|c|} \hline \text{column}\\ \hline \text{A}\\ \hline \text{B}\\ \hline \text{C}\\ \hline \text{A}\\ \hline \text{A}\\\hline \end{array} \rightarrow \begin{array}{|c|c|c|} \hline \text{A} & \text{B} & \text{C}\\ \hline 1 & 0 & 0\\ \hline 0 & 1 & 0\\ \hline 0 & 0 & 1\\ \hline 1 & 0 & 0\\ \hline 1 & 0 & 0\\\hline \end{array} \)
- 將測試資料轉成 multi-hot 型式:
import numpy as np def vectorize_sequences(sequences, dimension=10000): results = np.zeros((len(sequences), dimension)) for i, sequence in enumerate(sequences): results[i, sequence] = 1. return results x_train = vectorize_sequences(train_data) x_test = vectorize_sequences(test_data)- 將 labels 也轉成向量資料
y_train = np.asarray(train_labels).astype('float32') y_test = np.asarray(test_labels).astype('float32')
3. 建立神經網路
我們的輸入資料是向量、標籤為 0 與 1,我們可以使用一個密集層堆疊架構搭配 relu 函數。
我設計以下的三層神經網路架構:
\( \begin{array}{ccc} \text{輸入(向量化文字)}\\ \downarrow\\ \boxed{\text{密集(單元=16)}} & \text{relu} & \text{hidden layer}\\ \downarrow\\ \boxed{\text{密集(單元=16)}} & \text{relu} & \text{hidden layer}\\ \downarrow\\ \boxed{\text{密集(單元=1)}} & \text{softmax} & \text{output layer}\\ \downarrow\\ \text{輸出(預測值)}\\ \end{array} \)from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import layers model = keras.Sequential([ layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'), layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'), layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid') ])- compile
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])- 建立驗證集
x_val = x_train[:10000] partial_x_train = x_train[10000:] y_val = y_train[:10000] partial_y_train = y_train[10000:]- 訓練模型
history = model.fit(partial_x_train, partial_y_train, epochs=20 batch_size=512, validation_data=(x_val, y_val))- 繪製訓練與驗證圖
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt history_dict = history.history loss_values = history_dict['loss'] val_loss_values = history_dict['val_loss'] epochs = range(1, len(loss_values) + 1) plt.plot(epochs, loss_values, 'bo', label='Training loss') plt.plot(epochs, val_loss_values, 'b', label='Validation loss') plt.title('Training and validation loss') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Loss') plt.legend() plt.show()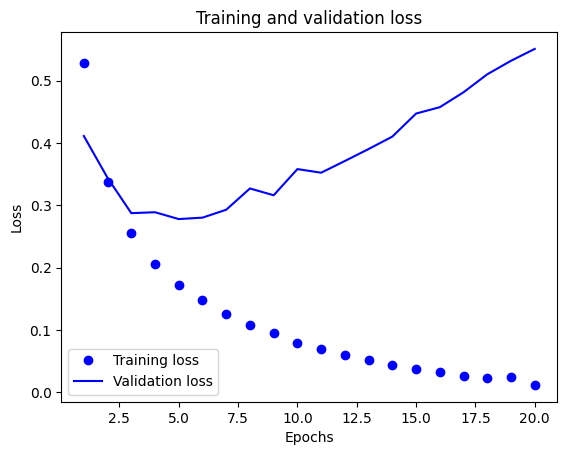
- 繪製訓練和驗證準確度
plt.clf() acc = history_dict['accuracy'] val_acc = history_dict['val_accuracy'] plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training accuracy') plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation accuracy') plt.title('Training and validation accuracy') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.legend()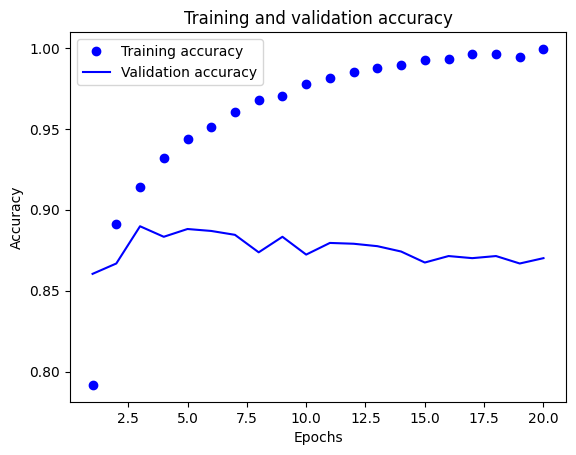
- 從結果可見,訓練集的損失隨訓練週期增加而減少,準確度隨週期增加而增加,但是對驗證集而言,卻沒有得到一樣的成效,這就是 過度配適(overfitting) 的現象。
- 我們可以使用其它技術來避免 overfitting 的發生,如 early stop、drop out
from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import layers from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping model = keras.Sequential([ layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'), layers.Dropout(0.5), layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'), layers.Dropout(0,5), layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid') ]) model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) early_stopping = EarlyStopping( monitor='val_loss', patience=4, # 連續4個epoch沒改善就停止 restore_best_weights=True # 回復最佳權重 ) x_val = x_train[:10000] partial_x_train = x_train[10000:] y_val = y_train[:10000] partial_y_train = y_train[10000:] history = model.fit(partial_x_train, partial_y_train, epochs=20, batch_size=512, validation_data=(x_val, y_val), callbacks=[early_stopping])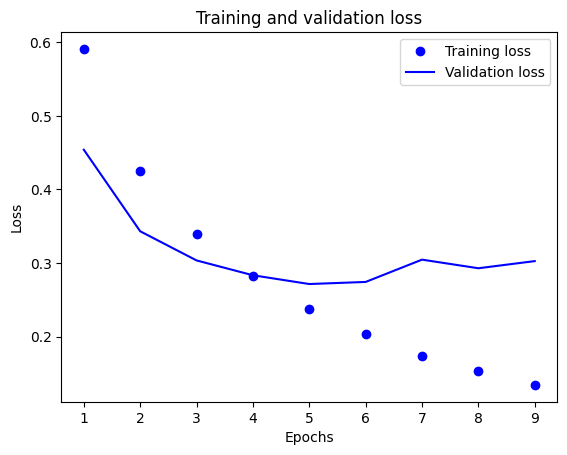
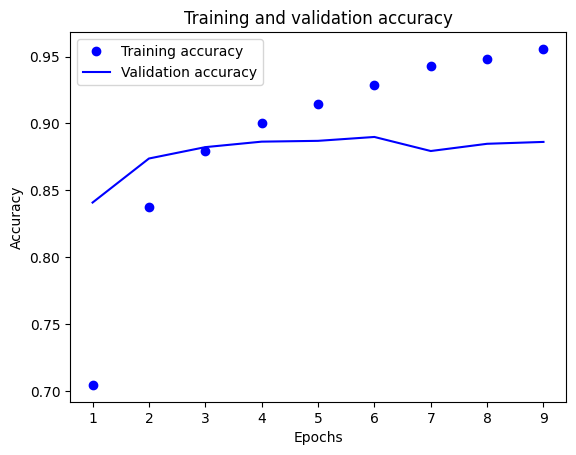
- 拿來測試驗證集
predictions = model.predict(x_test, batch_size=128) test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test) print(f'test_acc: {test_acc}') > test_acc: 0.8849200010299683