1235. Maximum Profit in Job Scheduling
- Hardness:
- Ralated Topics:
Array、Binary Search、Dynamic Programming、Sorting
一、題目
We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You’re given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1: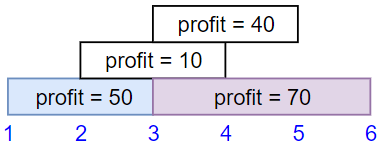
- Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70]
- Output: 120
- Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job.
Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
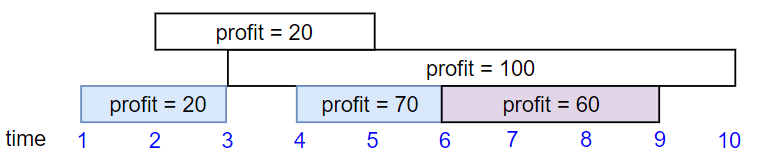
- Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60]
- Output: 150
- Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job.
Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
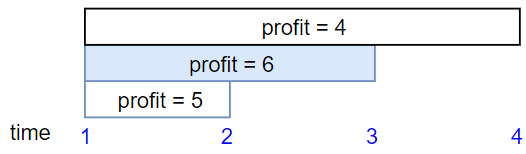
- Input: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
- Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 10^41 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 10^91 <= profit[i] <= 10^4
二、分析
- 在思考這一題,首先要先有
coin change的思維,也就是動態規劃:- 我們將
dp[n]定義為在時間n時的最大利益。 - 所以當時間點
i的最大利益會等於max(dp[i-1], dp[i - time_cost] + profit - 以範例 1 為例即:
dp[0] = 0dp[1] = 0dp[2] = 0dp[3] = 50 = max(dp[1]+50, dp[2])dp[4] = 50 = dp[3]dp[5] = 90 = max(dp[3]+40, dp[4])- …
- 其中我們可以發現,有可能發生改變的時間點都是在每一個工作的
endTime,也就是說我們只要針對每個endTime去記錄即可,其中我們可將dp[i - time_cost]改為搜尋小於startTime的最大值,即:dp[0] = 0dp[3] = 50 = max(dp[0], dp[3])dp[4] = 10 = max(dp[0]+10, dp[4])我們只記錄當下最大利益,故不記錄dp[5] = 90 = max(dp[3]+40, dp[5])dp[6] = 120 = max(dp[3]+70, dp[6]
- 我們將
- 我們可以使用
map這個資料結構,將所有trigger point依endTime排序後,逐步更新。- 其中注意
upper_bound(x)這個函式,會找大於x的位子,而且我們要找的是比小於等於當前startTime的資料,故我們找的是upper_bound(x)-1。 - 由於時間
t = 0時不會有收益,我們可以加入{0,0},這樣可以省去解決 iterator out of range(it 指向 -1) 的情形。
- 其中注意
三、解題
1. DP + Binary Search
- Time complexity:
- Space complexity:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
map<int,int> dp;
vector<vector<int>> job;
int n = startTime.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
job.push_back({endTime[i], startTime[i], profit[i]});
}
sort(job.begin(), job.end()); // sort by endTime
dp.insert({0,0}); // 省去處理 out of range
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
auto it = dp.upper_bound(job[i][1]); // > startTime
it--; // <= startTime
int last = it->second;
int val = last + job[i][2]; // 由當前最大收益往上累積
int pos = job[i][0];
if (val < res) continue; // 若當前最大收益比歷史最大收益還小,則跳過不記錄
dp[pos] = max(dp[pos], val); // 更新當前最大收益
res = max(dp[pos], res); // 更新歷史最大收益
}
return res;
}