124. Binary Tree Maximum Path Sum
- Hardness: \(\color{red}\textsf{Hard}\)
- Ralated Topics:
Dynamic Programming、Tree、Depth-First Search、Binary Tree
一、題目
- A path in a binary tree is a sequence of nodes where each pair of adjacent nodes in the sequence has an edge connecting them. A node can only appear in the sequence at most once. Note that the path does not need to pass through the root.
The path sum of a path is the sum of the node’s values in the path.
Given therootof a binary tree, return the maximum path sum of any non-empty path.
Example 1: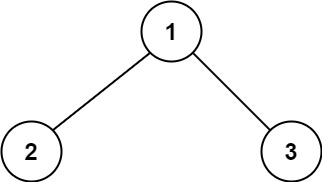
- Input: root = [1,2,3]
- Output: 6
- Explanation: The optimal path is 2 -> 1 -> 3 with a path sum of 2 + 1 + 3 = 6
Example 2:
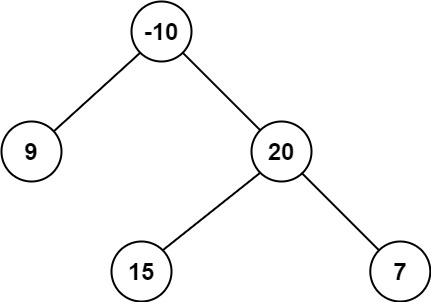
- Input: root = [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7]
- Output: 42
- Explanation: The optimal path is 15 -> 20 -> 7 with a path sum of 15 + 20 + 7 = 42.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3*10^4]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
二、分析
- 此題的解題關鍵在於求單邊子葉的最大
pathSum。 - 注意
pathSum只需要是路徑上的任一總和,無需一定要包含子葉節點。 - 對一個節點而言,可能的路徑包含:
- 節點本身
- 節點本身 + 左邊的
pathSum - 節點本身 + 右邊的
pathSum - 節點本身 + 兩邊的
pathSum
- 以上可以簡化成
root->val + max(leftPathSum, 0) + max(rightPathSum, 0)
- 故我們可以遍歷整棵樹,並同時更新可能的
三、解題
1. DFS
- Time complexity: \(O(n)\)
- Space complexity: \(O(1)\)
int res = INT_MIN;
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return res;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int left = dfs(root->left);
int right = dfs(root->right);
int sum = root->val + max(left, 0) + max(right, 0);
res = max(res, sum);
return root->val + max(max(left, 0) + max(right, 0));
}