1519. Number of Nodes in the Sub-Tree With the Same Level
- Hardness:
- Ralated Topics:
Hash Table、Tree、Depth-First Search、Breadth-First Search、Counting
一、題目
You are given a tree (i.e. a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 and exactly n - 1 edges. The root of the tree is the node 0, and each node of the tree has a label which is a lower-case character given in the string labels (i.e. The node with the number i has the label labels[i]).
The edges array is given on the form edges[i] = [ai, bi], which means there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return an array of size n where ans[i] is the number of nodes in the subtree of the ith node which have the same label as node i.
A subtree of a tree T is the tree consisting of a node in T and all of its descendant nodes.
Example 1: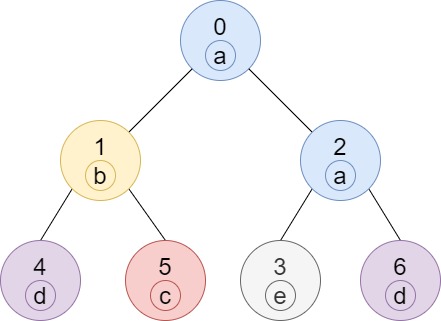
- Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], labels = “abaedcd”
- Output: [2,1,1,1,1,1,1]
- Explanation: Node 0 has label ‘a’ and its sub-tree has node 2 with label ‘a’ as well, thus the answer is 2. Notice that any node is part of its sub-tree.
Node 1 has a label ‘b’. The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1,4 and 5, as nodes 4 and 5 have different labels than node 1, the answer is just 1 (the node itself).
Example 2:
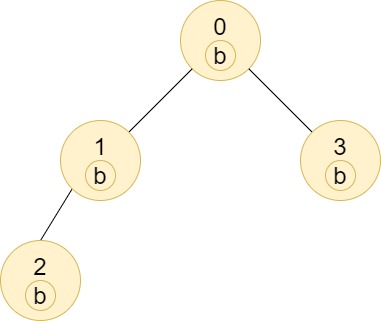
- Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,3]], labels = “bbbb”
- Output: [4,2,1,1]
- Explanation: The sub-tree of node 2 contains only node 2, so the answer is 1.
The sub-tree of node 3 contains only node 3, so the answer is 1.
The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1 and 2, both have label ‘b’, thus the answer is 2.
The sub-tree of node 0 contains nodes 0, 1, 2 and 3, all with label ‘b’, thus the answer is 4.
Example 3:
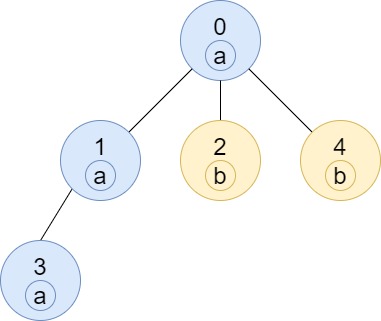
- Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[0,4]], labels = “aabab”
- Output: [3,2,1,1,1]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bilabels.length == nlabelsis consisting of only of lowercase English letters.
二、分析
- 這一題是後序遍歷,利用後序遍歷可以得到遍歷過後的訊息來解題。
- 我們要的訊息是:當遍歷完子節點之後,每個字元已出現了幾遍,而根節點以下的所有節點出現過的字元次數,就是所有子節點統計數字的相加再加上根節點自己。
- 這邊要注意的是,因為每次深入子節點,都需要新增一組陣列,會大量使用到記憶體,所以在處理上要小心空間複雜度的處理。技巧是,能用參考就用參考。
- 由於這題的
n的限制較大,只能運用陣列的加法,時間複雜度為,若場景有確認過,每個字符出現的次數限定在10以內,可以改用int來記錄,其加法的時間複雜度可以大大的下降。
三、解題
1. DFS
- Time complexity:
- Space complexity:
vector<int> res;
vector<int> countSubTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, string labels) {
vector<vector<int>> graph(n); // 先將 undirected graph 轉成每個節點有哪些鄰居
for (const auto& e : edges) {
graph[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
graph[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
res.assign(n, 0);
dfs(graph, labels, -1, 0); // 起點為 0,而節點不為負,過 last 可假定為任意負數
return res;
}
vector<int> dfs(vector<vector<int>>& graph, string& labels, int last, int curr) {
vector<int> path(26, 0); // 用一陣列記錄字符出現的次數
path[labels[curr]-'a']++;
for (const auto& next : graph[curr]) {
if (last == next) continue; // 進到上一輪的數字則跳過
vector<int> tmp = dfs(graph, labels, curr, next);
add(path, tmp); // 將遍歷完的結果加起來
}
res[curr] = path[labels[curr]-'a']; // 在後序的時間點,把統計完的結果記錄下來
return path;
}
void add(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) { // 用參考的方法做陣列的加法,也不回傳,可以省下空間
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
a[i] += b[i];
}