1706. Where Will the Ball Fall
- Hardness: \(\color{orange}\textsf{Medium}\)
- Ralated Topics:
Array、Dynamic Programming、Depth-First Search、Matrix、Simulation
一、題目
You have a 2-D grid of size m x n representing a box, and you have n balls. The box is open on the top and bottom sides.
Each cell in the box has a diagonal board spanning two corners of the cell that can redirect a ball to the right or to the left.
- A board that redirects the ball to the right spans the top-left corner to the bottom-right corner and is represented in the grid as
1. - A board that redirects the ball to the left spans the top-right corner to the bottom-left corner and is represented in the grid as
-1.
We drop one ball at the top of each column of the box. Each ball can get stuck in the box or fall out of the bottom. A ball get stuck if it hits a “V” shaped pattern between two boards or if a board redirects the ball into either wall of the box.
Return an arrayanswerof sizenwhereanswer[i]is the column that the ball falls out of at the bottom after dropping the ball from theithcolumn at the top, or-1if the ball gets stuck in the box.
Example 1: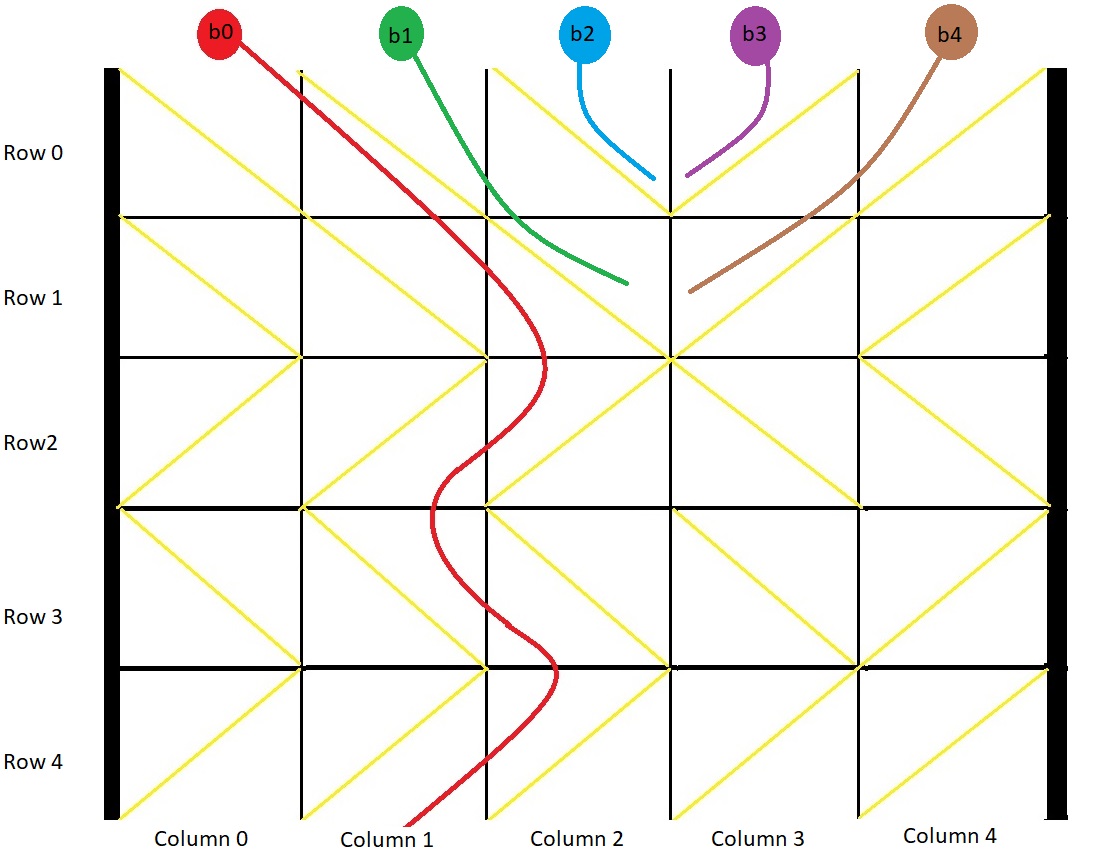
- Input: grid = [[1,1,1,-1,-1],[1,1,1,-1,-1],[-1,-1,-1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,-1],[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]]
- Output: [1,-1,-1,-1,-1]
- Explanation: This example is shown in the photo.
Ball b0 is dropped at column 0 and falls out of the box at column 1.
Ball b1 is dropped at column 1 and will get stuck in the box between column 2 and 3 and row 1.
Ball b2 is dropped at column 2 and will get stuck on the box between column 2 and 3 and row 0.
Ball b3 is dropped at column 3 and will get stuck on the box between column 2 and 3 and row 0.
Ball b4 is dropped at column 4 and will get stuck on the box between column 2 and 3 and row 1.
Example 2:
- Input: grid = [[-1]]
- Output: [-1]
- Explanation: The ball gets stuck against the left wall.
Example 3:
- Input: grid = [[1,1,1,1,1,1],[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1],[1,1,1,1,1,1],[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]]
- Output: [0,1,2,3,4,-1]
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100grid[i][j]is1or-1.
二、分析
- 這一題根據題意,球在落下的過程中,若碰到v-型或是牆,都會被卡住,可以歸納出下面幾條規則:(假設以
col代表球的位置)grid[row][0] == -1與grid[row][n-1] == 1代表撞到牆- 當
grid[row][col] == 1且grid[row][col+1] == 1時球可以落下。
或grid[row][col] == -1且grid[row][col-1] == -1時球可以落下。
三、解題
1. DP
- Time complexity: \(O(m\times n)\)
- Space complexity: \(O(n)\)
vector<int> findBall(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<int> state;
for (int col = 0; col < grid[0].size(); col++) state.push_back(col); // 初始化球當前的位置
for (auto& boards : grid) {
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (state[col] == -1) continue; // 球已經卡住了
int& pos = state[col];
if ((pos == 0 && boards[pos] == -1) || (pos == n-1 && boards[pos] == 1)) // 撞牆
pos = -1;
else if (boards[pos] == 1 && boards[pos+1] == 1) // 球往右移
pos += 1;
else if (boards[pos] == -1 && boards[pos-1] == -1) // 球往左移
pos -= 1;
else // 球卡住
pos = -1;
}
}
return state;
}
2. DFS
- Time complexity: \(O(m\times n)\)
- Space complexity: \(O(n)\)
int m, n;
vector<int> findBall(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<int> res(n);
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
res[col] = dfs(grid, 0, col);
}
return res;
}
int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int row, int col) {
if (row == m) return col; // 終止條件: 落地
if (col < 0 || col >= n) return -1; // 撞牆
if (col+1 < n && grid[row][col] == 1 && grid[row][col+1] == 1) // 右移
return dfs(grid, row+1, col+1);
if (col-1 >= 0 && grid[row][col] == -1 && grid[row][col-1] == -1) // 左移
return dfs(grid, row+1, col-1);
return -1;
}