872. Leaf-Similar Trees
- Hardness:
- Ralated Topics:
Tree、Depth-First Search、Binary Tree
一、題目
Consider all the leaves of a binary tree, from left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.
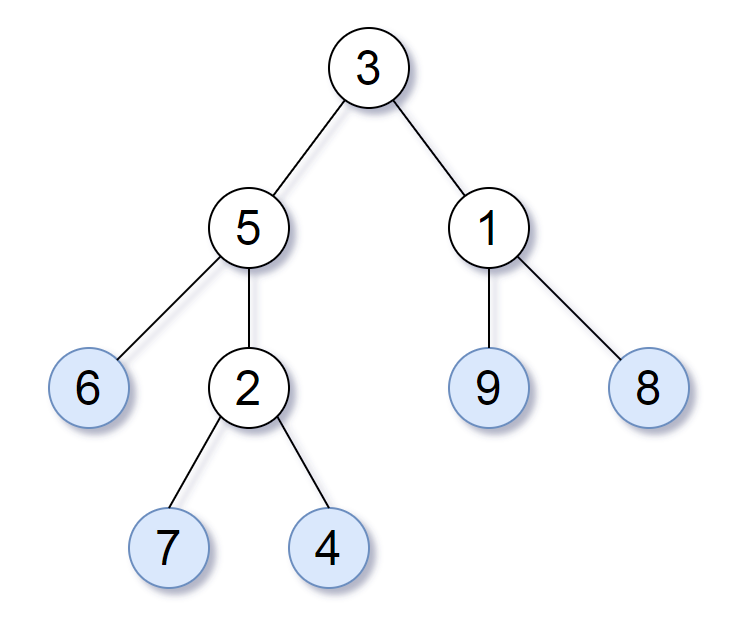 For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is (6, 7, 4, 9, 8).
Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return true if and only if the two given trees with head nodes root1 and root2 are leaf-similar.
Example 1: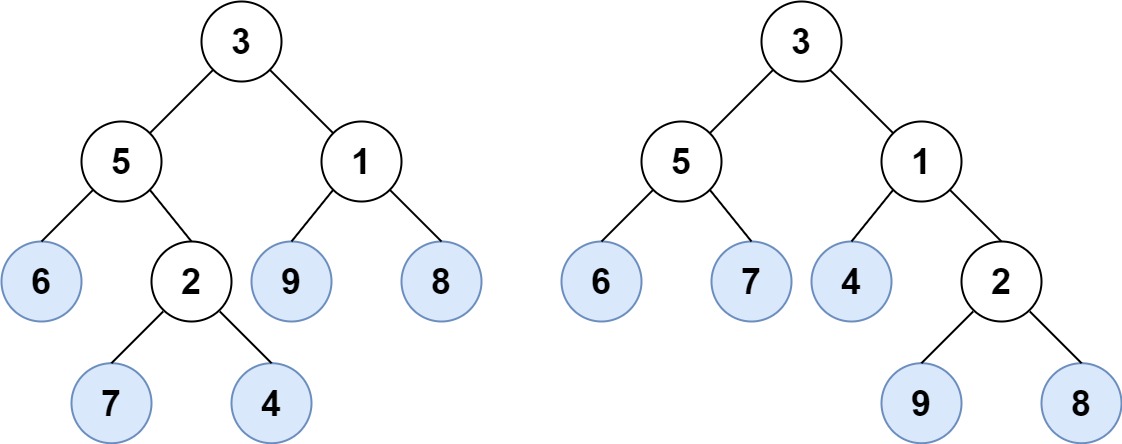
- Input: root1 = [3,5,1,6,2,9,8,null,null,7,4], root2 = [3,5,1,6,7,4,2,null,null,null,null,null,null,9,8]
- Output: true
Example 2:
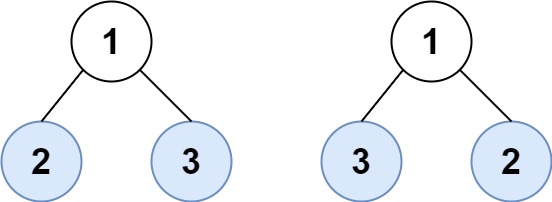
- Input: root1 = [1,2,3], root2 = [1,3,2]
- Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree will be in the range
[1, 200]. - Both of the given trees will have values in the range
[0, 200].
二、分析
- 將所有的節點遍歷過一遍,並將所有的子葉節點記錄在
vector中,再逐一比較即可。
三、解題
1. DFS
- Time complexity:
- Space complexity:
bool leafSimilar(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
vector<int> vec1, vec2;
dfs(root1, vec1);
dfs(root2, vec2);
return isSame(vec1, vec2);
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& vec) {
if (!root) return;
if (!root->left && !root->right) vec.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->left, vec);
dfs(root->right, vec);
}
bool isSame(vector<int>& vec1, vector<int>& vec2) {
if (vec1.size() != vec2.size()) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < vec1.size(); i++) {
if (vec1[i] != vec2[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}