931. Minimum Falling Path Sum
- Hardness: \(\color{orange}\textsf{Medium}\)
- Ralated Topics:
Array、Dynamic Programming、Matrix
一、題目
Given an n x n array of integers matrix, return the minimum sum of any falling path through matrix.
A falling path starts at any element in the first row and chooses the element in the next row that is either directly below or diagonally left/right. Specifically, the next element from position (row, col) will be (row + 1, col - 1), (row + 1, col), or (row + 1, col + 1).
Example 1: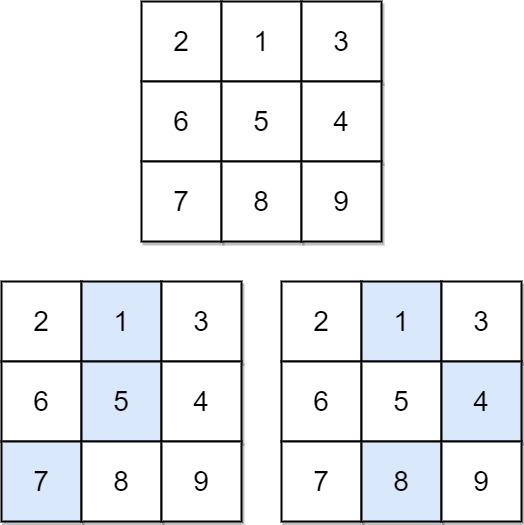
- Input: matrix = [[2,1,3],[6,5,4],[7,8,9]]
- Output: 13
- Explanation: There are two falling paths with a minimum sum as shown.
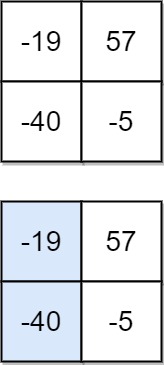 Example 2:
Example 2:
- Input: matrix = [[-19,57],[-40,-5]]
- Output: -59
- Explanation: The falling path with a minimum sum is shown.
Constraints:
n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length1 <= n <= 100-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
二、分析
- 這題也是典型的動態規劃問題,每一層可能的最小值,會影響到下一層的最小值,所以我們只需記錄每一層的狀態再將狀態往下一層推移即可。
- 定義
dp[m][n]為第m層,第n欄的累計最小值。 - 轉移方程式為
dp[m][n] = min({dp[m-1][n-1], dp[m-1][n], dp[m-1][n+1]}) + row[m][n]。- 但要注意最左邊跟最右邊要另外處理以避免出界。
- 從轉移方程式可以注意到,狀態的轉移只跟上一層有關係,故可以做空間壓縮,就空間複雜度壓到 \(O(n)\)
三、解題
1. DP
- Time complexity: \(O(m\times n)\)
- Space complexity: \(O(m\times n)\)
int minFallingPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
if (m == 1) return matrix[0][0];
vector<vector<int>> dp(m+1, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
vector<int>& row = matrix[i];
dp[i+1][0] = min(dp[i][0], dp[i][1]) + row[0];
dp[i+1][n-1] = min(dp[i][n-1], dp[i][n-2]) + row[n-1];
for (int j = 1; j < n-1; j++) {
dp[i+1][j] = min({dp[i][j-1], dp[i][j], dp[i][j+1]}) + row[j];
}
}
int res = INT_MAX;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
res = min(res, dp[m][j]);
}
return res;
}
2. DP space-optimized
- Time complexity: \(O(m\times n)\)
- Space complexity: \(O(n)\)
int minFallingPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
if (m == 1) return matrix[0][0];
// 利用奇數層跟偶數層做切換
vector<vector<int>> dp(2, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < m-1; i++) {
vector<int>& row = matrix[i];
dp[i%2][0] = min(dp[(i+1)%2][0], dp[(i+1)%2][1]) + row[0];
dp[i%2][n-1] = min(dp[(i+1)%2][n-1], dp[(i+1)%2][n-2]) + row[n-1];
for (int j = 1; j < matrix[0].size()-1; j++) {
dp[i%2][j] = min({dp[(i+1)%2][j-1], dp[(i+1)%2][j], dp[(i+1)%2][j+1]}) + row[j];
}
}
int res = INT_MAX;
dp[(m-1)%2][0] = min(dp[m%2][0], dp[m%2][1]) + matrix[m-1][0];
dp[(m-1)%2][n-1] = min(dp[m%2][n-1], dp[m%2][n-2]) + matrix[m-1][n-1];
res = min({res, dp[(m-1)%2][0], dp[(m-1)%2][n-1]});
for (int j = 1; j < matrix[0].size()-1; j++) {
dp[(m-1)%2][j] = min({dp[m%2][j-1], dp[m%2][j], dp[m%2][j+1]}) + matrix[m-1][j];
res = min(res, dp[(m-1)%2][j]);
}
return res;
}