基本邏輯運算
Logic Gates
Not Gates
- Symbol
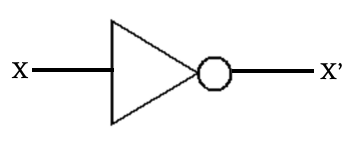
- Truth Table
\( \def\arraystrecth{1.5}\begin{array}{|c|c|}\hline \text{X}&\overline{\text{X}}\text{or}\text{X’}\\\hline 0&1\\\hline 1&0\\\hline \end{array} \)
And Gates
- Symbol
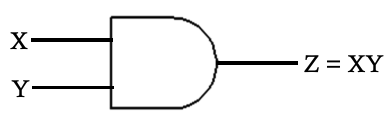
- Truth Table
\( \def\arraystrecth{1.5}\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}\hline \text{X}&\text{Y}&\text{Z=X}\cdot\text{Y}\\\hline 0&0&0\\\hline 0&1&0\\\hline 1&0&0\\\hline 1&1&1\\\hline \end{array} \)
Or Gates
- Symbol
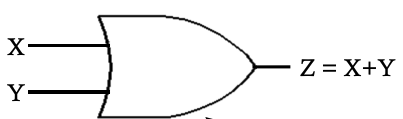
- Truth Table \( \def\arraystrecth{1.5}\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}\hline \text{X}&\text{Y}&\text{Z=X+Y}\\\hline 0&0&0\\\hline 0&1&1\\\hline 1&0&1\\\hline 1&1&1\\\hline \end{array} \)
布林表達式與真值表(Boolean Expression and Truth Table)
- Boolean expression
- 用
'代表 NOT - 用
+代表 OR - 用
.代表 AND - 將輸入用上面的運算子表示成算式,如:\((A+C)(B’+C)\)
- 用
- Truth Table \( \def\arraystrecth{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc|cccccc} A&B&C&B’&AB’&AB’+C&A+C&B’+C&(A+C)(B’+C)\\\hline 0&0&0&1&0&0&0&1&0\\ 0&0&1&1&0&1&1&1&1\\ 0&1&0&0&0&0&0&0&0\\ 0&1&1&0&0&1&1&1&1\\ 1&0&0&1&1&1&1&1&1\\ 1&0&1&1&1&1&1&1&1\\ 1&1&0&0&0&0&1&0&0\\ 1&1&1&0&0&1&1&1&1\\ \end{array} \)
基本運算定理
NOT gate 的基本運算定理
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} (x’)’&=&x \end{array} } \)
AND gate 的基本運算定理
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} x+0&=&x\\ x+1&=&1\\ x+x&=&x\\ x+x’&=&1 \end{array} } \)
OR gate 的基本運算定理
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} x\cdot 0&=&0\\ x\cdot 1&=&x\\ x\cdot x&=&x\\ x\cdot x’&=&0 \end{array} } \)
進階運算定理
交換律 Commutative Law
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} xy&=&yx\\ x+y&=&y+x \end{array} } \)
結合律 Associative Law
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} (xy)z&=&x(yz)\\ (x+y)+z&=&x+(y+z) \end{array} } \)
分配律 Distributive Law
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} x(y+z)&=&xy+xz\\ x+yz&=&(x+y)(x+z) \end{array} } \)
Multiplying out and factoring
Sum of Product(SOP) form
- 將算式化整成各個輸入端先 AND 後再 OR
- 例: \(ABC+AB’C+AB’C’\)
Product of Sum(POS) form
- 將算式化整成各個輸入端先 OR 後再 AND
- 例: \((A+B+C)(A+B’+C)(A+B’+C’)\)
Multiplying out:
- 將算式化簡成 SOP form
- 善用\(\boxed{(A+B)(A+C)=A+BC}\)
- 範例:
\((A+BC)(A+D+E)\)
\(=(A+x)(A+y)\)
\(=A+xy\)
\(=A+BC(D+E)\)
\(=A+BCD+BCE\)
Factoring:
- 將算式化簡成 POS form
- 善用\(\boxed{A+BC=(A+B)(A+C)}\)
- 範例:
\(AB’+C’D\)
\(=(AB’+C’)(AB’+D)\)
\(=(A+C’)(B’+C’)(A+D)(B’+D))\)
2-level realization
- 利用 Multiplying out 與 Factoring 可以將電路簡化成 2-level circuit
- 因為減少了 Delay propagation 可以減少 Total Time Delay
DeMorgan’s Laws and Duality
DeMorgan’s Laws
- 方法:
- \(AND\leftrightarrow OR\)
- \(A\leftrightarrow A’\)
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} (x+y+z+…)’&=&x’ y’ z’…\\ (xyz…)’&=&x’+y’+z’… \end{array} } \)
- Truth Table 證明
\( \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc|ccc|c|c|c} x&y&z&x’&y’&z’&x+y+z&(x+y+z)’&x’ y’ z’\\\hline 0&0&0&1&1&1&0&1&1\\ 0&0&1&1&1&0&1&0&0\\ 0&1&0&1&0&1&1&0&0\\ 0&1&1&1&0&0&1&0&0\\ 1&0&0&0&1&1&1&0&0\\ 1&0&1&0&1&0&1&0&0\\ 1&1&0&0&0&1&1&0&0\\ 1&1&1&0&0&0&1&0&0\\ \end{array} \) - 範例
\([(A’ B+C’)(D’+EF’)+GH+W]’\)
\(=[(A+B’)C+D(E’+F)] (G’+H’)W’\)
Duality
方法
- \(AND\leftrightarrow OR\)
- \(0\leftrightarrow 1\)
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{cccccccccc} [f(&x_1,&x_2,&…,&x_n,&0,&1,&+,&\cdot&)]^D\\ =f(&x_1,&x_2,&…,&x_n,&1,&0,&\cdot,&+&) \end{array} } \)
性質
- \(\boxed{F=G\rightarrow F^D=G^D}\)
範例
\((x+y’)y=xy\rightarrow x\cdot y’+y=x+y\)回顧分配律 Distributive Law,即為 Duality 的表現。
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} x(y+z)&=&xy+xz\\ x+yz&=&(x+y)(x+z) \end{array} } \)
Exclusive-OR and equivalence operations
Exlusive-OR(XOR,\(\oplus\))
- Symbol
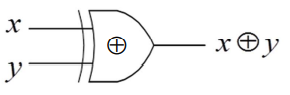
- Truth Table
\( \def\arraystrecth{1.5}\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}\hline \text{X}&\text{Y}&\text{Z=X}\oplus\text{Y}\\\hline 0&0&0\\\hline 0&1&1\\\hline 1&0&1\\\hline 1&1&0\\\hline \end{array} \) - 性質:
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} x\oplus 0&=&x\\ x\oplus 1&=&x’\\ x\oplus x&=&0\\ x\oplus x’&=&1\\ x\oplus y&=&y\oplus x\\ (x\oplus y)\oplus z&=&x\oplus (y\oplus z)\\ x(y\oplus z)&=&xy\oplus xz\\ x\oplus y&=&xy+x’ y' \end{array} } \)
Equivalence(\(\equiv\))
- Symbol
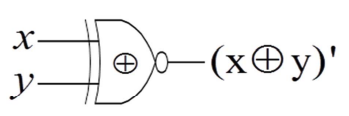
- Truth Table
\( \def\arraystrecth{1.5}\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}\hline \text{X}&\text{Y}&\text{Z=X}\equiv{Y}\\\hline 0&0&1\\\hline 0&1&0\\\hline 1&0&0\\\hline 1&1&1\\\hline \end{array} \) - 性質:
\( \boxed{ \def\arraystretch{1.5}\begin{array}{ccc} x\equiv 0&=&x’\\ x\equiv 1&=&x\\ x\equiv x&=&1\\ x\equiv x’&=&0\\ x\equiv y&=&y\equiv x\\ (x\equiv y)\equiv z&=&x\equiv (y\equiv z)\\ x(y\equiv z)&=&xy\equiv xz\\ x\equiv y&=&xy’+x’ y \end{array} } \)
連鎖律 The consensus thorem
- 公式:
- \(\boxed{xy+x’ z+yz=xy+x’ z}\)
- \(\boxed{(x+y)(x’+z)(y+z)=(x+y)(x’+z)}\)
- 證明:
\(xy+x’ z+yz\)
\(=xy+x’ z + (x+x’)yz\)
\(=xy+xyz+x’ z+x’ yz\)
\(=xy(1+z)+x’ z(1+y)\)
\(=xy+x’ z\)
簡化布林表達式的流程
- 利用 \(\boxed{xy+xy’=x(y+y’)=x}\)(AND性質)
- 利用 \(\boxed{x+xy+…=x(1+y+…)=x}\)(OR性質)
- 利用 \(\boxed{xy+x’ z+yz=xy+x’z }\)(連鎖律)
- 利用 \(\boxed{x+x’y=x(y+y’)+x’y=xy+xy’+x’ y=x+y}\)
- 必要時加入 redundant terms
- Lec3會使用圖表法,較不容易出錯。
如何證明布林表達式的正確性?
- 建構 Truth Table
- 簡化 LHS 和 RHS
